|
Classification of Plasmas |
|
|
|
Physics of High Energy Densities |
|
High-Energy-Density / Strongly Coupled Systems |
|
Classification of Plasmas |
|
|
|
Typical Parameters of High-Energy-Density Systems |
|||||
| Density | 100 - 105 | [solid] | Temperature | 105 - 109 | K |
| Electric field | 1010 - 1014 | V/m | Energy density | 1010 - 1018 | J/m3 |
| Energy flux | 1019 - 1024 | W/m2 | Time scale | 10-15 - 10-8 | s |
|
Evolution of Heavy and Medium Stars |
|
Neutron Stars : Milisecond Pulsar |
|
Astrophysical Condensed Plasmas |
||
| Density [ g / cm^3] | Temperature [ K ] | |
|
Sun |
||
| Average | 1.41 | |
| Central part | 1.56 x 10^2 | 1.5 x 10^7 |
| Very low mass stars | ||
| Central part | 10^2 - 10^3 | (2 - 3 ) x 10^6 |
| Giant Planets | ||
| Average | 2 - 5 | 5 x 10^3 - 2 x 10^4 |
| White dwarfs | ||
| Average | 10^6 | |
| Central | 10^7 - 10^10 | 10^7 - 10^9 |
| Neutron stars | ||
| Outer crust | 10^4 - 10^7 | 10^7 |
|
Laser Drivers for ICF & HED Physics |
|
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory : Laser System Nova |
|
|
|
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: NIF (November 2000) |
 |
|
|
|
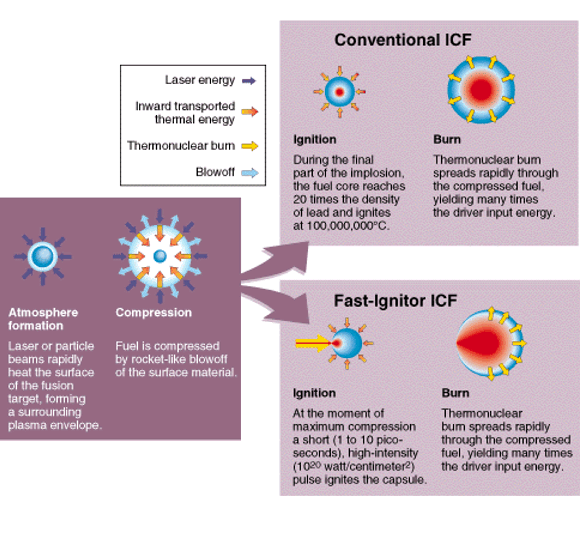
Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF) |
|
Conventional and Fast-Ignitor Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF) |
 |